With a highly customized architecture and manufactured on TSMC’s N3E node, Xiaomi’s new XRING O1 chip achieves an outstanding balance of performance, energy efficiency, and density, marking a milestone for China’s semiconductor industry.
Xiaomi has officially entered the elite ranks of processor design with its new XRING O1 SoC, first used in the Xiaomi 15S Pro and the Xiaomi Pad 7 Ultra. Far from being a simple ARM reference design, the XRING O1 features a custom CPU and NPU architecture, unconventional cache configurations, and a balanced approach that has achieved unprecedented efficiency per square millimeter of silicon, surpassing giants like Apple, Qualcomm, and MediaTek.
Performance with Architectural Intelligence
Manufactured on TSMC’s N3E node, just like its closest competitors, the XRING O1 features two Cortex-X925 cores, an unusual detail (the norm is usually just one), alongside six Cortex-A725 cores, divided into two clusters: four for high performance and two for energy efficiency. It also includes two Cortex-A520 cores, although the efficiency of the A725 makes these almost unnecessary.
This hybrid architecture enables dynamic power scaling, adapting consumption to real-time use. The result: a CPU that’s faster and more energy-efficient than that of the Dimensity 9400, and not far behind Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite.
A Compact and Dense Design
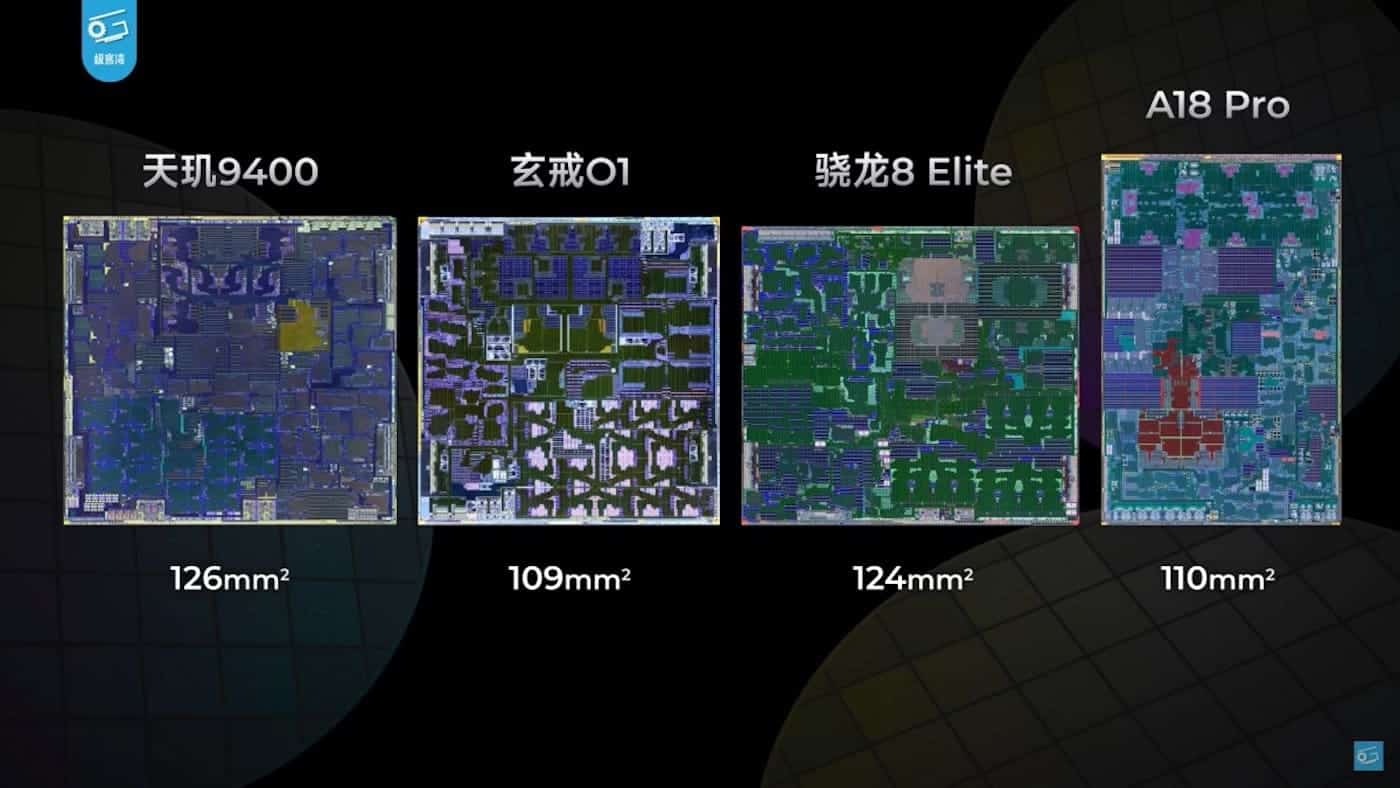
At only 109 mm², the XRING O1 is smaller than most of its rivals: Dimensity 9400 (126 mm²), Snapdragon 8 Elite (124 mm²), and nearly equal to the Apple A18 Pro (110 mm²). However, Xiaomi has managed to include a 16-core GPU, a six-core NPU, a fourth-generation ISP, and a performance-oriented cache hierarchy without using System Level Cache (SLC), which Apple and MediaTek do.
According to initial tests, the XRING O1 achieves 88.7 points of efficiency in performance per mm², surpassing the A18 Pro (85.2), the Snapdragon 8 Elite (82.6), and leaving the Dimensity 9400 (73.9) behind, demonstrating that the Chinese architecture has matured to compete globally in the high-end market.
Areas for Improvement: GPU and External Modem
Not everything is perfect: the 16-core ARM Immortalis-G925 GPU, while powerful, consumes more energy than MediaTek’s, especially since it lacks SLC to assist sustained graphics performance. Additionally, the XRING O1 does not integrate a 5G modem, instead relying on an external MediaTek T800, which penalizes battery life on the Xiaomi 15S Pro.
Apple has already addressed this with its integrated 5G modem in the iPhone 16e, and Xiaomi seems ready to follow the same path: it recently unveiled the Xring T1, its first proprietary 4G modem for the Xiaomi Watch S4. The leap to 5G will be complex, but it’s a step toward vertical integration.
A Clear Message to the Industry
The XRING O1 represents the most balanced SoC on the market in terms of performance, size, and efficiency, an achievement that marks a turning point for Xiaomi and, by extension, for China’s semiconductor industry. With this launch, the company positions itself not just as a hardware manufacturer, but as an architecture designer capable of competing with Apple, Qualcomm, or MediaTek on their own turf.
If Xiaomi can successfully integrate a modem and improve graphics efficiency in future generations, we could be witnessing the rise of a new global silicon giant.
via: GSMarena