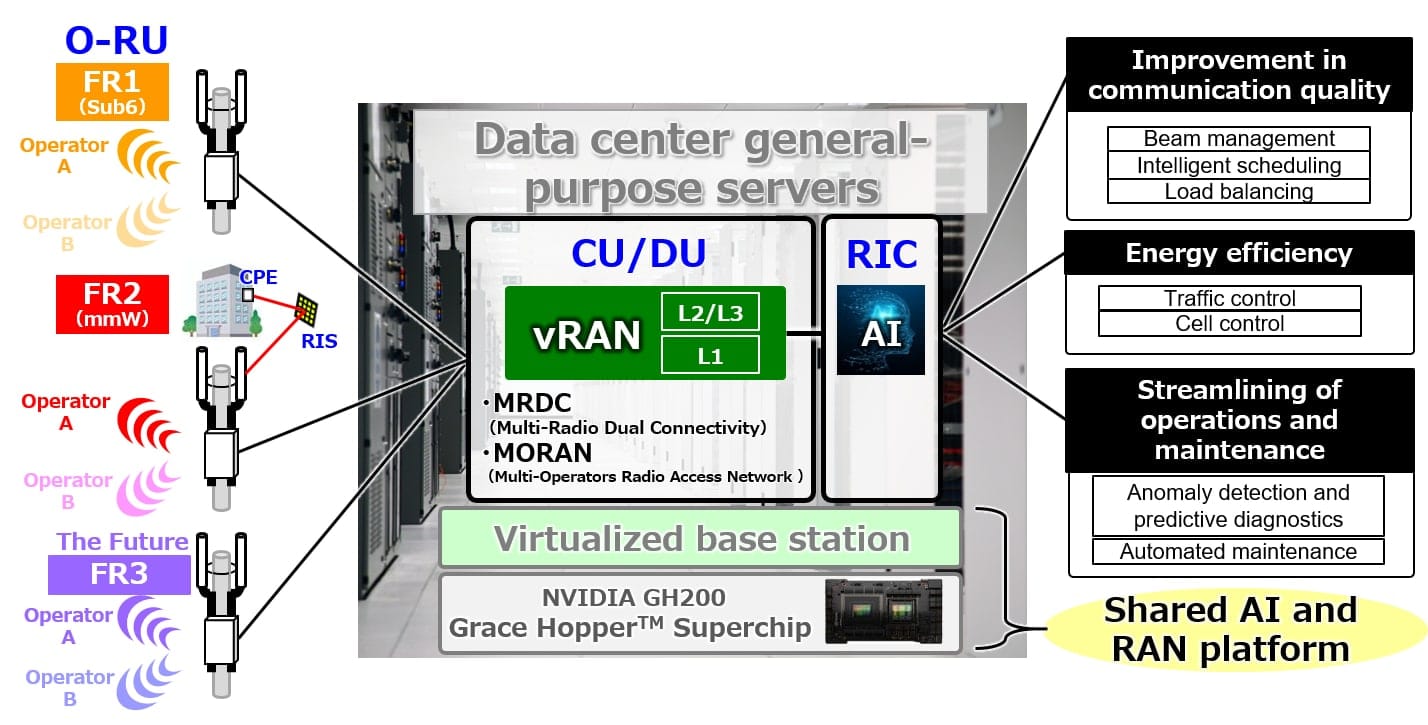
The Japanese company develops a virtualized base station with artificial intelligence to optimize networks and reduce energy consumption.
Kyocera Corporation has announced the large-scale development of a virtualized 5G base station powered by artificial intelligence (AI), aiming to commercialize the technology in the coming months. The initiative seeks to revolutionize telecommunications infrastructure by enhancing network performance, optimizing energy consumption, and simplifying operational management.
The rollout of 5G networks has become a key pillar of global digital transformation. In this context, Kyocera is betting on the virtualization of base stations through general-purpose servers, utilizing the NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip. This approach will allow operators to implement more efficient and scalable networks, aligning with the standards of the O-RAN Alliance, which promotes interoperability in radio access networks.
Key Innovations of Kyocera’s 5G Base Station
1. AI Optimization
The system integrates AI to enhance traffic management, optimizing frequency allocation and ensuring faster upload and download speeds. Additionally, AI monitors network demand in real-time, dynamically adjusting energy consumption to improve operational efficiency. Automation of configurations and adjustments allows for more agile and efficient network management.
2. Dual Connectivity: Sub-6 GHz and Millimeter Waves
Kyocera has developed a solution compatible with O-RAN specifications, enabling the simultaneous management of two frequency bands: Sub-6 GHz and millimeter waves. The combination of both frequencies through an accelerated computing server facilitates a faster response to traffic spikes and allows for future software upgrades to support new spectrum bands.
3. Base Station Sharing Among Operators
One of the standout innovations in Kyocera’s proposal is the capability for base station sharing. With this advancement, multiple operators can use a single centralized unit (CU/DU or O-RU) to process data, significantly reducing the number of necessary stations. This optimization not only decreases infrastructure and energy consumption costs but also facilitates the expansion of 5G coverage in hard-to-reach areas.
4. Coverage Expansion and Energy Consumption Reduction
Thanks to the implementation of advanced software, Kyocera’s solution allows for the front-haul distance to be extended to over 40 kilometers, improving coverage in rural and densely populated urban areas. The consolidation of CU/DU units into a single server also reduces energy consumption, contributing to a more sustainable network.
Kyocera at Mobile World Congress 2025
Kyocera will showcase its virtualized base station at the Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2025, which will take place in Barcelona from March 3 to 6. At this event, the company will present its advancements in 5G infrastructure and demonstrate how its AI- and virtualization-based technology can transform the telecommunications sector.
Glossary of Key Terms
- RAN (Radio Access Network): A radio access network that enables wireless communication via radio waves.
- CU (Central Unit): The central component of the access network that manages data processing and function control.
- DU (Distributed Unit): The unit responsible for processing wireless signals in real-time within the access network.
- RU (Radio Unit): The device that sends and receives radio signals, acting as the physical communication interface.
- O-RU (Open Radio Unit): A radio unit compliant with O-RAN standards, designed to allow interoperability between different manufacturers.
- O-RAN Alliance: A global organization that promotes openness and intelligence in radio access networks, facilitating their interoperability.
With this new development, Kyocera is positioning itself as a key player in the evolution of the 5G ecosystem, focusing on efficiency, sustainability, and flexibility in future telecommunications networks.