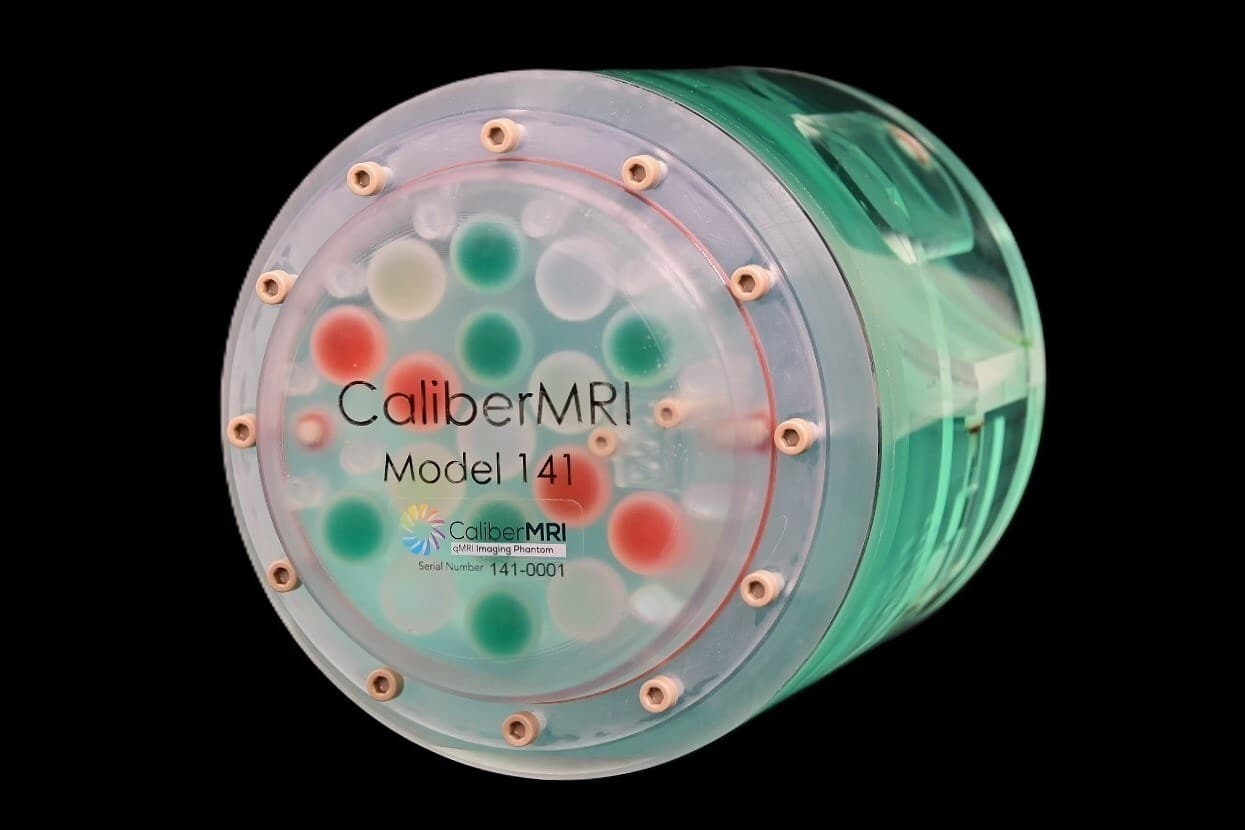
CaliberMRI, a company specializing in MRI standardization, has announced the launch of qDisc (Quantitative Dual Imaging Standardization Compartment) Model 141, a new quantitative phantom designed to work alongside the classic ACR medium phantom (American College of Radiology). Its goal: transforming a routine quality control test into a much more powerful tool capable of generating quantitative metrics ready for advanced research and AI algorithms.
From simple visual validation to comprehensive quantitative metrics
Traditionally, the ACR Medium Phantom has been used in hospitals and imaging centers to qualitatively verify that an MRI scanner meets ACR standards: geometry, spatial resolution, uniformity, basic contrast, etc.
The new qDisc Model 141 physically integrates into this same workflow: scanned alongside the ACR phantom and, in a single slice, it provides reference values for four key parameters in quantitative MRI (qMRI):
- T1 (longitudinal relaxation time)
- T2 (transverse relaxation time)
- ADC (apparent diffusion coefficient)
- Proton Density (PD)
This combination allows centers to move from “seeing if the image looks good” to quantitatively measuring how the scanner responds — essential when comparing results across different machines, hospitals, or protocols, or training AI models with consistent data.
Integrated thermometer and automated analysis
The qDisc also incorporates the patented CaliberMRI LC thermometer that is MR-readable, enabling precise measurement of the phantom’s temperature during acquisition. This is critical because parameters like T1 and T2 depend on temperature: uncontrolled, reference values can vary and lose their comparative utility.
All generated data is processed with qCal-MR®, CaliberMRI’s automated QA/QC software, which analyzes images, extracts quantitative metrics, and produces reports ready for medical physicists, radiologists, or research teams. This reduces manual work and minimizes errors in interpreting results.
According to the company, the qDisc is designed as an “additional layer” on top of existing ACR controls: it does not replace the firm’s full phantoms but serves as a practical entry point for centers wanting to start standardizing qMRI without overhauling their routines.
A key step toward harmonizing qMRI (and AI in medical imaging)
The announcement comes at a time when quantitative MRI is becoming a cornerstone of clinical research and medical AI. Being able to compare T1, T2, or ADC across machines, hospitals, and countries is crucial for building robust models to:
- detect early disease,
- monitor treatment progress,
- or train AI algorithms with high-quality multi-parameter data.
CaliberMRI emphasizes that their phantom and software platforms support more than 45 scanner models and manufacturers, from 0.064 T to 7 T systems, making them a technical infrastructure suited for multicenter studies and large consortia.
Based in Boulder, Colorado, the company has collaborated for years with organizations such as NIST, RSNA, and ISMRM on developing standards and reference phantoms, and its products are cited in over 200 scientific articles and abstracts related to qMRI.
Context: why is standardizing MRI so important in the AI era
In many hospitals, MRI still relies heavily on qualitative assessment: radiologists interpret images based on their experience. However, there is growing interest in measuring reproducible quantitative parameters — like T1, T2, or ADC — which enable:
- longitudinal studies of the same patient,
- standardization across centers,
- and feeding clinical decision support systems powered by AI.
The challenge is that these values can vary significantly between scanners, protocols, and manufacturers if acquisition and calibration conditions are not carefully controlled. Quantitative phantoms provide “reference truths” to validate whether a machine is measuring what it claims to measure.
In this context, solutions like qDisc facilitate that validation in daily clinical practice, leveraging ACR scans that many centers already perform due to regulatory requirements or quality practices.
RSNA 2025 as a showcase
CaliberMRI will present the qDisc and its entire family of quantitative phantoms at the RSNA Congress, held in Chicago from November 30 to December 3, at booth 7610 in the North Hall. RSNA is one of the key events of the year in medical imaging and often acts as a thermometer for emerging trends in radiology and AI in imaging.
From medical physics to clinical AI
While the announcement is clearly targeted at medical physicists and quality managers in radiology departments, the broader implications are:
- For research centers, it offers a relatively simple way to ensure their MRI data are comparable with other groups.
- For hospitals and healthcare networks, it can be an internal audit tool and a means to harmonize their scanner fleets.
- For companies developing AI in medical imaging, well-calibrated and traceable quantitative datasets are almost a prerequisite to move from prototypes to regulated products.
Thus, the qDisc fits into a broader trend: shifting from “artisanal” radiology to a more measurable, standardized, and AI-ready paradigm that maintains clinical relevance.
CaliberMRI highlights that this new phantom is not an endpoint but a first step toward more comprehensive qMRI platforms that cover additional parameters, geometries, and use cases. But it marks an important milestone: bringing quantification and AI preparation into routine quality assurance, without requiring a complete overhaul of workflows.