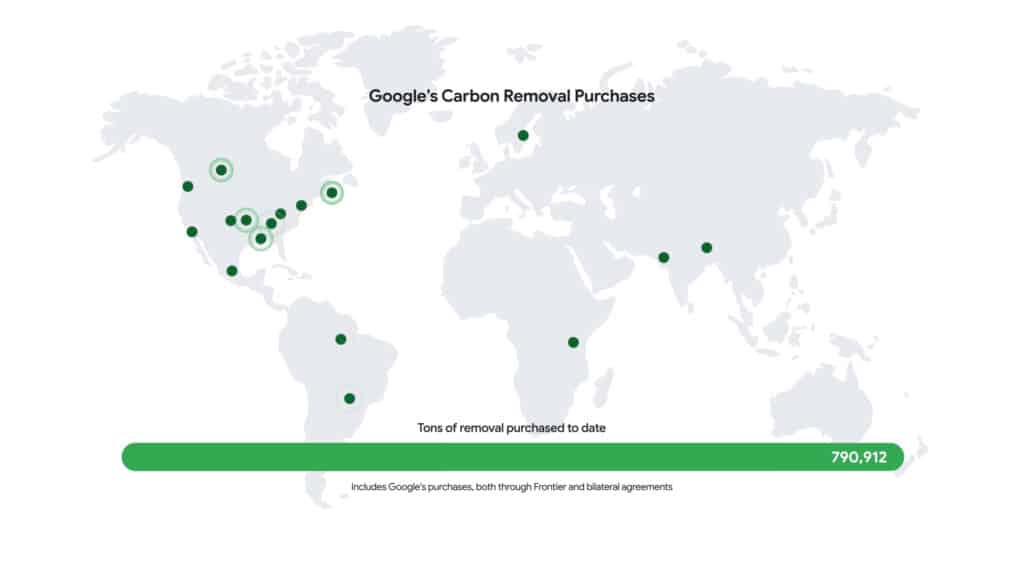
Google has intensified its commitment to the fight against climate change by investing over $100 million in carbon removal credits during 2024, tripling its initial promise. Through a combination of direct purchases and agreements with the Frontier consortium, the company aims to accelerate innovative solutions for CO₂ reduction and contribute to the expansion of scalable technologies for carbon capture and storage.
Four Key Approaches to Carbon Removal
Google’s strategy to reduce its carbon footprint focuses on multiple fronts, from restoring natural sinks to developing new technologies.
1. Restoring Natural Carbon Sinks with Rigorous Measurement
Oceans and forests play a crucial role in absorbing CO₂, but their impact has been difficult to quantify. To address this issue, Google co-founded Symbiosis, a market commitment that sets rigorous criteria for forestry projects and facilitates their scalability. Additionally, through Frontier, it has funded initiatives like CarbonRun, aimed at improving the health of aquatic ecosystems while removing carbon from the atmosphere.
2. Promoting Rock Weathering to Capture CO₂
Rock weathering is a natural process that traps CO₂ in geological formations for millennia. Applying crushed rocks to agricultural soils can accelerate this phenomenon, while also benefiting soil health. Google has supported Terradot and other providers of this technique in various regions around the world, aiming to enhance the measurement and deployment of this solution.
3. Biomass Capture to Prevent Carbon Release
Billions of tons of biomass decompose every year, releasing CO₂ into the atmosphere. Google is funding projects to utilize this waste and mitigate its environmental impact, from carbon capture initiatives in industrial infrastructures like CO280 to biochar projects like Varaha and Charm, which also generate economic benefits for farming communities.
4. Developing More Cost-Effective Direct Air Capture Technologies
Technological solutions also play a crucial role in large-scale carbon removal. Direct Air Capture (DAC) is one of the most promising alternatives, but it requires a significant reduction in costs to be viable in the long term. Google has backed emerging technologies like Holocene, which established the lowest price to date for DAC credits, and 280 Earth, a project incubated within Alphabet X, the company’s innovation division.
A Long-Term Commitment to a Cleaner Planet
While Google has taken significant steps in carbon removal, it recognizes that this is just the beginning of a global effort. To achieve real impact, it is essential that other companies, researchers, and governments join this initiative and collaborate in developing sustainable solutions.
“We know that Google cannot lead these efforts alone. We need other stakeholders, from companies to academics, to come together to drive large-scale solutions with a meaningful impact on the atmosphere,” stated Randy Spock, head of carbon credits and removal at Google.
As the company moves toward its goal of net-zero emissions, it will continue to explore new opportunities to mitigate climate change and maximize the benefits of carbon removal worldwide.